The Seven Steps
Emergency Power System
Purpose
To secure emergency power systems.
The emergency power system can include the following elements:
- Motor generator set
- Battery set
- Fuel supply tank
- Muffler
- Electric cable
- Power transfer unit
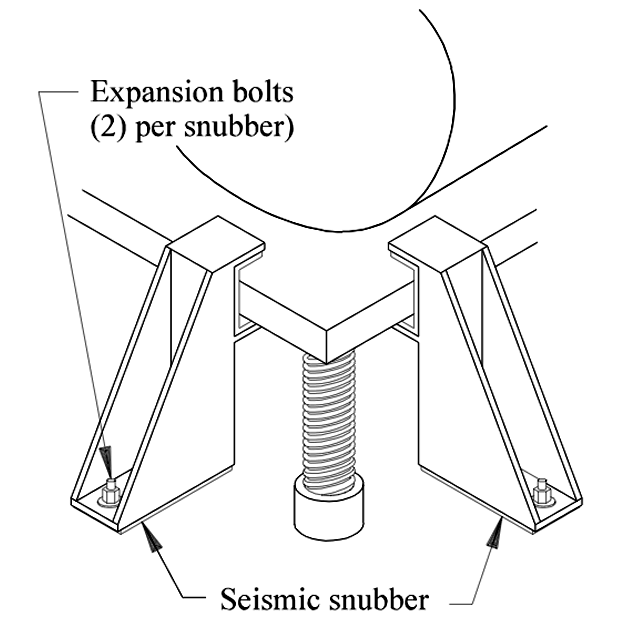
Recommendation — Secure Generator
Supplies Required
- Eight steel Z snubbers (or other type of seismic snubber)
- Eight expansion bolts—1/2″ diameter (for concrete)
OR
Eight expansion bolts—1/2″ diameter (for wood)
Installation
- Place snubbers at two sides near the corners.
- Bolt to the concrete or wood, allowing 1″ free play between the generator and snubber.
Note
- Due to size or complex design, motor generator sets and power transfer units may require more extensive mitigation design by a structural engineer.
- Equipment may already be anchored directly without using isolation springs. Consult with structural engineer to determine if seismic snubbers are necessary.
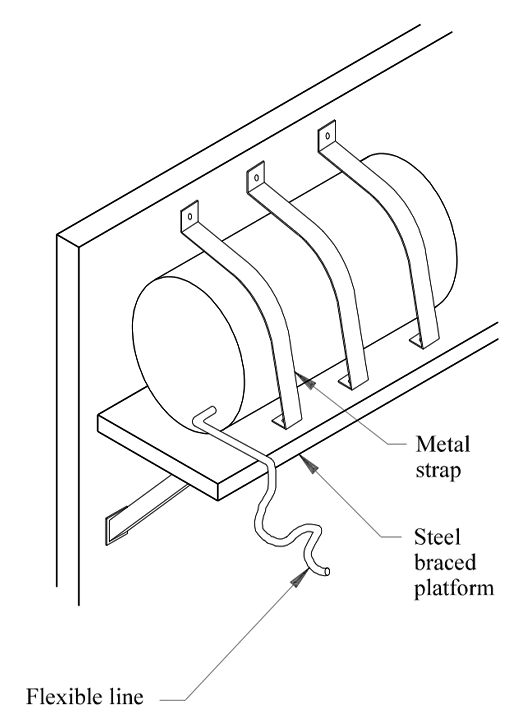
Recommendation — Secure Fuel/Water Tank
Install steel braced platforms, metal straps, and slack line to secure fuel supply tank or water day tank.
Caution
When anchoring to post-tensioned slab, locate and avoid reinforcing.
Supplies Required
- Steel-braced platform (Consult an engineer for design.)
- Metal straps (18 gage x 2″)
- Sheet metal screws—3/8″
- Flexible line
- Lag bolts or expansion bolts—3/8″
Installation
- Place a minimum of two straps (one at each end of the tank).
- Secure straps to the steel-braced platform with sheet metal screws. Attach to supporting structure with lag bolts or expansion bolts.
Note
- Provide slack in electrical cables.
- Anchor each element in the system.